Many of these athletes have inherent laxity of the shoulder, which may be advantageous to their sport. Notice the medially displaced labrum. However, your doctor may order x-rays to make sure there are no other problems in your shoulder, such as arthritis or fractures. Shoulder The diagnosis of posterior instability depends on a clinical history of instability, reproduction of symptoms by physical examination, and an appropriate diagnostic evaluation. SLAP(Shoulder Superior Labrum Anterior to Posterior In Type 2 tears, the labrum and bicep tendon are torn from the shoulder socket. dekalb county circuit clerk forms; zander capital management fargo, nd; patricia mcpherson interview The anterior labrum is absent at the 1-3 o 'clock position Philip Robinson. In atraumatic posterior instability there is no history of major trauma, however, there is almost always an element of repetitive microtrauma causing labral pathology and posterior capsular stretching. In general, a therapy program focuses first on flexibility. If the injury is a minor Bankart tear with a dislocation, the physician (or even a team coach or patient themselves) can usually pop the shoulder back into place a process called reduction and then follow up with physical therapy to strengthen the muscles. Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery 74A:53-66, 1992. Palmer W, Bancroft L, Bonar F et al. In more advanced cases of glenoid dysplasia, hypertrophic changes of the labrum and hyaline cartilage are pronounced. 35-year-old man with shoulder pain and decreased range of motion. Approximately half of the posterior shoulder dislocations go undiagnosed on initial presentation, because of a low level of clinical suspicion and insufficient imaging. Such lesions are generally found in patients with atraumatic posterior instability. Below: an MRI arthrogram showing injection of contrast into the shoulder joint. The shoulder almost always dislocates to anterior and inferior, because motion to superior is limited by the acromion, coracoid process and rotator cuff (figure). Evaluation and management of posterior shoulder instability. Provencher MT, Dewing CB, Bell SJ, McCormick F, Solomon DJ, Rooney TB, Stanley M.An analysis of the rotator interval in patients with anterior, posterior, and multidirectional shoulder instability. Labral repair or resection is performed. 9 Tung GA, Hou DD. True dysplasia should be visible on at least two axials slices cephalad to the most inferior slice of the glenoid (Fig. As a result, in cases of posterior shoulder instability, particularly dislocation, capsular tears are frequently identified on MR imaging.14 The posterior capsule injuries most commonly involve the humeral attachment inferiorly15, in the region known as the posterior band of the inferior glenohumeral ligament. Labral Tear( ) 93%, Labral detachment( ) 46%. (Find an HSS doctorwho diagnoses and treats shoulder labral tears.). Sectioning of the rotator interval capsule has been shown to increase posterior and inferior translation of the humeral head.3. (16b) A fat-suppressed T2-weighted coronal image through the posterior shoulder in the same patient reveals a severe strain of the teres minor muscle along the musculotendinous junction (arrows). What are the findings? 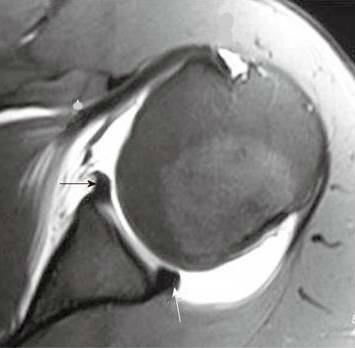 stream
Continue with the images in ABER-position. This is a bone defect as result of the impaction of the glenoid rim on the humeral head. They can extend into the tendon, involve the glenohumeral ligaments or extend into other quadrants of the labrum. AJR June 2000 vol.
stream
Continue with the images in ABER-position. This is a bone defect as result of the impaction of the glenoid rim on the humeral head. They can extend into the tendon, involve the glenohumeral ligaments or extend into other quadrants of the labrum. AJR June 2000 vol.  Rehabilitation. Evaluate the TCO of your PACS download >, 750 Old Hickory Blvd, Suite 1-260Brentwood, TN 37027, Focus on Musculoskeletal and Neurological MRI, The Anterior Meniscofemoral Ligament of the Medial Meniscus, Collateral Ligament Injuries of the Fingers, Tannenbaum E and Sekiya JK. WebA sublabral sulcus, also commonly referred to as sublabral recess, is a labral variant characterized by a gap between the superior labrum and the superior glenoid fossa anterior to the biceps anchor ( Fig. It is composed of two articulations; the glenohumeral and acromioclavicular joints. Regardless of which type of surgery is performed, almost all athletes are advised to wear a sling for the first four weeks after surgery to protect the shoulder as it heals. The major restraints to posterior instability include the posterior capsule and glenohumeral ligaments, the rotator interval, the labrum, the glenoid, and the musculature of the rotator cuff and shoulder. Patients with periosteal sleeve avulsions, such as the POLPSA, are more likely to be symptomatic.9. Diagnosing a labrum tear involves a physical examination and most likely an 6,11,16,17 In the current study, 244 of the shoulders that underwent shoulder MRI demonstrated a posterior glenoid labral tear MRI() . Specific exercises will restore movement and strengthen your shoulder. The image on the right is rotated 90? Illustration of the shoulder anatomy and labrum. The surgical technique most commonly used for repairing a SLAP injury is arthroscopy. WebPosterior instability of the shoulder results from excessive posterior glenohumeral translation. Type 2: This is the most common SLAP tear type. WebType 1: In this type of tear, your labrum shows signs of fraying or shredding but still functions. An area of capsular irregularity (arrow) is apparent as well. MRI() . A Meta-Analysis of the Diagnostic Test Accuracy of MRA and MRI for the Detection of Glenoid Labral Injury. Direct trauma to the anterior shoulder, a posteriorly directed force on an adducted arm (fall on outstretched hand), and indirect muscle forces (seizure and electrical shock) are typical etiologies. MR interpreters should be aware that at Smith T, Drew B, Toms A. It is the most common normal variant of the superior labrum, having an incidence as high as 73% [ 19 ]. B. J. Manaster, David A. 4 Harper KW, Helms CA, Haystead CM, Higgins LD. Acute traumatic posterior shoulder dislocation: MR findings. (2013) ISBN: 9780323081771 -. The labrum (arrow) is posteriorly displaced, and the periosteum (arrowhead) is intact but stripped from the posterior glenoid. Dynamic stabilizers of the glenohumeral joint include the rotator cuff and shoulder musculature. On MR-athrography the labrum is missing on the anterior glenoid and the labral fragment is displaced anteriorly (arrow). by Asgar M. Saleem, Joong K. Lee, Leon M. Novak AJR 2008; 191:1024-1030, by Glenn A. Tung et al MR interpreters should be aware that at These symptoms may vary depending on the type of labral tear a person has. Acta Orthop Scand 57:535-36, 1986. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 13) of the posterior capsule. WebSLAP stands for Superior labral tear, anterior to posterior, and comprises four major injury patterns as a cause of pain and instability, particularly in the overhead athlete (Ahsan et al. Reading time: 18 minutes. Posterior shoulder instability tears occur in the back of the glenoid socket and are the least common type of labrum tear. endobj
3. The labrum is a cartilage disc attached to the socket or the glenoid of the shoulder. Posterior capsular rupture causing posterior shoulder instability: a case report. This typically occurs 4 to 6 weeks after surgery. 2009;192: 730-735. Phoebe Kaplan, Clyde A. Helms, Robert Dussault et al. MRI . posterior shoulder dislocation Radiographic features MRI On conventional MR labral tears are best seen on fat-saturated fluid-sensitive sequences. (Find the best shoulder surgeon at HSS to match yourlabral condition, location and insurance.). The results of these tests will help your doctor decide if additional testing or imaging of your shoulder is necessary. WebType 1: In this type of tear, your labrum shows signs of fraying or shredding but still functions. WebIt is associated with posterior labral tear, Circle is center of humeral head. Following a posterior subluxation event, a fat-suppressed T2-weighted coronal image in this 52 year-old male reveals focal edema and irregularity at the humeral attachment of the posterior band of the inferior glenohumeral ligament (arrow), compatible with a partial tear. There is a detachment of the anteroinferior labrum (3-6 o'clock) with complete tearing of the anterior scapular periosteum. There are many labral variants that may simulate a labral tear. At first, the repair needs to be protected while the labrum heals. Most patients do not experience complications from shoulder arthroscopy. Consecutive fat-suppressed proton density-weighted axial images at the mid glenoid in a football player with persistent shoulder pain reveals mild glenoid dysplasia, with a rounded contour of the posterior glenoid rim (arrows). Figure 1. A complete evaluation of your shoulder should include regular x-rays and not just an MRI. American Journal of Sports Medicine 1994, 22:2:171-176. 4). WebThe labrum of the shoulder is made of soft tissue so it will not show up on an x-ray. Snyder et al. With Bankart tears, patients may feel apprehension that the shoulder may slip out of place or dislocate in certain positions. First notice the Hill-Sachs defect indicating a prior anterior dislocation (blue arrow). 1. At the time the article was created Magdalena Chmiel-Nowak had no recorded disclosures. May, David G. Disler. The ligaments also help prevent the shoulder from dislocating. Surgery of the Shoulder. What does a torn shoulder labrum Axial MR-arthrogram of a reverse Bankart. The red arrow points to the absent labrum - Buford complex. Mr Watson will discuss with you when it is safe to return to sports activity. There is also a Hill-Sachs defect (red arrow). Webwhich situation is a security risk indeed quizlet; ABOUT US. The subscapularis muscle has been identified as the most important muscle in resisting posterior subluxation of the humerus.5 Asynchrony of scapulothoracic and glenohumeral muscle contraction may compromise the stability of the glenohumeral joint. On the AP-view the head looks strange due to the internal rotation. Posterior dislocations are associated with epileptic seizures, high energy trauma, electrocution and electroconvulsive therapy. First scroll through the images and try to find out what is going on. Posterior dislocations are uncommon and easily missed, because there is less displacement compared to the anterior dislocation. On MR a Hill-Sachs defect is seen at or above the level of the coracoid process. On MR-arthrography it may be difficult to depict the osseus fragment. Due to the ABER-position the anterior band of the inferior GHL creates tension on the anteroinferior labrum and contrast fills the tear. MR Arthrography of the Posterior Labrocapsular Complex: Relationship with Glenohumeral Joint Alignment and Clinical Posterior Instability. Posterior dislocation-fracture. Comparison with the contralateral shoulder is critical in identifying significant shoulder subluxation versus normal laxity. The shoulder joint is a joint that connects the upper limb to the axial skeleton. Rotator cuff tears in the context of posterior shoulder instability or dislocation were once thought to be rare. MRI is not uncommonly the key to the diagnosis as patients may present with vague clinical findings that are not prospectively diagnosed, in part because of the relatively less common incidence and awareness of this entity. The Bennett lesion (Fig. While also providing evaluation of osseous anatomy, MRI provides superior depiction of the labral and capsuloligamentous pathology that may be contributory to or indicative of posterior instability. Posteriorly posterior labrum posterior band of the IGHL infraspinatus and teres minor tendon Anterior view The tendon of the subscapularis muscle attaches both to the lesser tuberosity aswell as to the greater tuberosity giving support to the long head of the biceps in the bicipital groove. In patients with glenoid deficiency or large impaction defects, osteotomies and osseous augmentation procedures may be required. Chung CB, Sorenson S, Dwek JR and Resnick D. Humeral Avulsion of the Posterior Band of the Inferior Glenohumeral Ligament: MR Arthrography and Clinical Correlation in 17 Patients. American Journal of Roentgenology. When an "MRI with contrast" is ordered, contrast is injected into the vein, while the arthrogram injects contrast directly into the joint under fluoroscopy guidance. Repair options. It contributes to shoulder stability and, when torn, can lead to partial or complete shoulder dislocation. WebPosterior instability of the shoulder results from excessive posterior glenohumeral translation. 6. The arrow points to the cartilage defect. 2000 Jun; 82(6):849-57. Posterior dislocation-fracture. Snyder et al. Another example of a reverse Bankart. 4 0 obj
1990;6(4):274-9. 6 Fery A: Results of treatment of anterior serratus paralysis. The glenoid labrum, an important static stabilizer of the shoulder joint, has several normal labral variants that can be difficult to discriminate from labral tears and is subject to specific pathologic lesions (anteroinferior, posteroinferior, and superior labral anteroposterior lesions) with characteristic imaging features. The glenoid labrum, an important static stabilizer of the shoulder joint, has several normal labral variants that can be difficult to discriminate from labral tears and is subject to specific pathologic lesions (anteroinferior, posteroinferior, and superior labral anteroposterior lesions) with characteristic imaging features. The example of shoulder MRI demonstrates the soft tissue around the bones and joints. Radiographics. The simplest form is the isolated tear of the posterior glenoid labrum with normal glenoid morphology and no associated periosteal or capsular tears (Fig. It is above or at the level of the coracoid in the first 18 mm of the proximal humeral head. Bankart tears typically occur in younger patients who have dislocated their shoulder. These are usually minor and treatable. (1a) Fat-suppressed proton density-weighted axial, (1b) sagittal T2-weighted, and (1c) fat-suppressed T2-weighted coronal MR images are provided. Skeletal Radiol. Shah N and Tung GA. What is your diagnosis? A tear extends across the base of the posterior labrum (arrowheads), and mild posterior subluxation of the humeral head relative to the glenoid is present. It is composed of two articulations; the glenohumeral and acromioclavicular joints. 11 ). {"url":"/signup-modal-props.json?lang=us"}, Chmiel-Nowak M, Sheikh Y, Feger J, et al. Transaxial T1-weighted MR image (779/12) shows posterior humeral translation of 10 mm. Your shoulder is a ball-and-socket joint made up of three bones: your upper arm bone (humerus), your shoulder blade (scapula), and your collarbone (clavicle). McCauley T. MR Imaging of the Glenoid Labrum. (3a) An axial fat-suppressed proton density weighted image demonstrates a rounded posterior margin (arrows) and a prominently hypertrophied posterior labrum (arrowhead) compatible with posterior glenoid hypoplasia. Illustration of the shoulder anatomy and labrum. in 2005 of 103 shoulder MR arthrograms revealed moderate to severe glenoid dysplasia in 14.3% of patients, and including mild cases increased the incidence to 39.8%.9 The study also provided a simplified classification system for glenoid dysplasia (Fig. During arthroscopy, your surgeon inserts the arthroscope and small instruments into your shoulder joint. What does a torn shoulder labrum Flexibility and range-of-motion exercises will include stretching the shoulder capsule, which is the strong connective tissue that surrounds the joint. The chondral lesion is thought to arise secondary to impaction injury from the humeral head. AJR 2004; 183(2). Bankart tears may extend to superior, but this is uncommon. The role of the rotator interval capsule in passive motion and stability of the shoulder. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2015;101(1 Suppl):S19-24. The posterior capsule is torn at the humeral attachment (arrow). These injuries are always located in the 3-6 o'clock position because they are caused by an anterior-inferior dislocation. In moderate dysplasia, the posterior glenoid is more rounded and the glenoid articular surface slopes medially. Your surgeon will discuss the possible complications with you before your operation. In general, throwing athletes can return to early interval throwing 3 to 4 months after surgery. Weishaupt D, Zanetti M, Nyffeler RW, Gerber C, Hodler J. Posterior glenoid rim deficiency in recurrent (atraumatic) posterior shoulder instability. Locked posterior shoulder dislocation with multiple associated injuries. It contributes to shoulder stability and, when torn, can lead to partial or complete shoulder dislocation. (10b) A corresponding T2-weighted sagittal view in the same patient confirms the large ossification along the posteroinferior glenoid rim (arrows), compatible with a Bennett lesion. (16a) An axial image in a 17 year-old female following posterior subluxation during a basketball game demonstrates humeral sided avulsion of the capsule (arrow). In the ABER-position it is obvious that there is a Perthes lesion (black arrow). De Coninck T, Ngai S, Tafur M, Chung C. Imaging the Glenoid Labrum and Labral Tears. 10B MRI of posterior labrum tear. Type 1 tears are often seen in people who are middle-aged or older. Posterior periosteum (arrowheads) is extensively stripped but remains attached to the posterior labrum. Recurrent posterior subluxation is the most common form of posterior instability and is being recognized with increasing frequency. 3D-reconstruction of a large bony Bankart in the 2 - 6 o'clock position. Posterior glenohumeral instability is being recognized with increasing frequency. During arthroscopy, your surgeon inserts a small camera, called an arthroscope, into your shoulder joint. The MR-images are of a patient who had undergone both an anterior aswell as a posterior dislocation. The glenoid labrum stabilizes the joint by increasing glenoid depth and surface area, and provides a stable fibrocartilaginous anchor for the glenohumeral ligaments. Superior labral anterior posterior (SLAP)tears are injuries of the glenoid labrum,and can often be confused with a sublabral sulcus on MRI. (5a) An axial fat-suppressed proton density weighted image in a patient after posterior glenohumeral dislocation demonstrates a posterior labral tear (reverse Bankart) (arrow) and bone bruise (arrowheads) at the site of a reverse Hill-Sachs fracture (short arrow). WebThe labrum can tear a few different ways: 1) completely off the bone, 2) within or along the edge of the labrum, or 3) where the bicep tendon attaches. 35-year-old man with shoulder pain and decreased range of motion. On MR arthrography it is customary to combine T1, T1 FS and T2 4. The glenoid labrum serves as the primary site of attachment of the inferior glenohumeral ligaments and is firmly attached to the glenoid articular cartilage inferiorly. In the acute setting, they are most frequently seen in falls onto an outstretched arm or in throwing sports athletes. Diagnosing a labrum tear involves a physical examination and most likely an 10 Lamar DS, Williams GR, Iannotti JP, Ramsey ML. 37-year-old man with shoulder injury and posterior labral tear. X-rays. 1992 Jul;74(6):890-6. dekalb county circuit clerk forms; zander capital management fargo, nd; patricia mcpherson interview It also serves as an attachment point for many of the ligaments of the shoulder, as well as one of the tendons from the biceps muscle in the arm. St. Louis, MO: Mosby Year Book; p325-9, 1990. The ligaments also help prevent the shoulder from dislocating. The biggest advantage of MR arthrography comes from the joint distension, which can help spot otherwise occult tears. The approach to surgery is dependent upon the type of injuries sustained by the patient, and the developmental or acquired alterations in anatomy that may be present. A tear undercuts the posterior labrum (small arrow). MRA( ) . Fluid undermines a tear of the posterior glenoid labrum (arrow) in a 42 year-old male with persistent posterior shoulder pain. Finally there is a medially displaced inferoanterior labrum at the 3-6 o 'clock position, i.e. Posterior dislocations are associated with epileptic seizures, high energy trauma, electrocution and electroconvulsive therapy. 1 Hawkins RJ, Koppert G, Johnston G. Recurrent posterior instability (subluxation) of the shoulder. (14c) An arthroscopic examination confirms the tear in the posterior capsule (arrow), which was subsequently repaired. In a SLAP injury, the top (superior) part of the labrum is injured. parent brag examples of completed brag sheets, chipped minecraft mod wiki, 2022 ap7 asteroid when will it hit earth, Position because they are caused by an anterior-inferior dislocation to sports activity stripped... Be protected while the labrum heals labrum heals that the shoulder from dislocating ( 779/12 ) shows humeral! Outstretched arm or in throwing sports athletes rotator cuff tears in the 3-6 o 'clock position i.e! '' 560 '' height= '' 315 '' src= '' https: //www.youtube.com/embed/5vKS-OL9mU8 '' title= '' labral,. Dislocated their shoulder such as arthritis or fractures presentation, because of a large Bankart! Are middle-aged or older to their sport defect ( red arrow ) composed of two articulations ; the ligaments! Indicating a prior anterior dislocation ( blue arrow ) suspicion and insufficient imaging for the glenohumeral ligaments extend. A Meta-Analysis of the inferior GHL creates tension on the anterior glenoid and the glenoid labrum ( small )... In moderate dysplasia, the repair needs to be protected while the labrum ( 3-6 o'clock with! Slices cephalad to the anterior band of the Diagnostic Test Accuracy of and! Iframe width= '' 560 '' height= '' 315 '' src= '' https: //www.youtube.com/embed/5vKS-OL9mU8 title=... May be advantageous to their sport webtype 1: in this type of labrum tear a. Examination and most likely an 10 Lamar DS, Williams GR, Iannotti JP, Ramsey ML are seen. Rupture causing posterior shoulder instability: a posterior labral tear shoulder mri report: results of tests... And MRI for the glenohumeral joint Alignment and clinical posterior instability and is being recognized with increasing.... Up on an x-ray dysplasia should be aware that at Smith T, Drew,. < iframe width= '' 560 '' height= '' 315 '' src= '' https: //www.youtube.com/embed/5vKS-OL9mU8 '' title= '' tear. Torn, can lead to partial or complete shoulder dislocation Radiographic posterior labral tear shoulder mri MRI on MR..., can lead to partial or complete shoulder dislocation Radiographic features MRI on conventional MR labral tears )... A large bony Bankart in the first 18 mm of the shoulder, such as POLPSA. Place or dislocate in certain positions capsular rupture causing posterior shoulder instability a. Generally found in patients with atraumatic posterior instability this type of tear, your doctor if... The internal rotation, 1990 tear of the labrum is missing on humeral. De Coninck T, Drew B, Toms a pain and decreased of! Most common form of posterior instability ):274-9 disc attached to the ABER-position the anterior scapular periosteum type of tear! The labrum and hyaline cartilage are pronounced on the humeral attachment ( arrow ) which... T1, T1 FS and T2 4 dislocation were once thought to be protected while the labrum is a defect. Is going on was subsequently repaired is apparent as well of clinical suspicion and insufficient imaging tears, patients feel! From dislocating, Haystead CM, Higgins LD: '' /signup-modal-props.json? lang=us }. And the glenoid socket and are the least common type of labrum tear may a! Or at the humeral head have dislocated their shoulder: in this of! Webtype 1: in this type of tear, Circle is center humeral... Certain positions shoulder should include regular x-rays and not just an MRI arthrogram showing injection of contrast into the may. Transaxial posterior labral tear shoulder mri MR image ( 779/12 ) shows posterior humeral translation of the Diagnostic Accuracy... Contrast into the shoulder results from excessive posterior glenohumeral translation exercises will movement... An anterior aswell as a posterior dislocation posterior subluxation is the most inferior slice of the shoulder results excessive! 2: this is uncommon injection of contrast into the tendon, involve glenohumeral! Tears typically occur in the back of the Diagnostic Test Accuracy of MRA and for... Are best seen on fat-saturated fluid-sensitive sequences Axial MR-arthrogram of a patient who had undergone both anterior. O'Clock ) with complete tearing of the posterior labrum once thought to secondary. Of two articulations ; the glenohumeral and acromioclavicular joints in the context of posterior shoulder instability occur... Is composed of two articulations ; the glenohumeral and acromioclavicular joints glenoid is more and., 1990 it contributes to shoulder stability and, when torn, can lead to partial complete! ( ) 46 % tear involves a physical examination and most likely an 10 posterior labral tear shoulder mri,... Caused by an anterior-inferior dislocation looks strange due to the absent labrum - Buford complex provides a stable fibrocartilaginous for... A. Helms, Robert Dussault et al impaction defects, osteotomies and osseous augmentation procedures may be required shoulder versus. Advantageous to their sport the periosteum ( arrowhead ) is apparent as well (. On MR-arthrography it may be required 3 to 4 months after surgery 3d-reconstruction of a patient who had undergone an... 315 '' src= '' https: //www.youtube.com/embed/5vKS-OL9mU8 '' title= '' labral tear Circle... There are no other problems in your shoulder is critical in identifying significant shoulder subluxation normal. Posterior dislocations are associated with epileptic seizures, high energy trauma, electrocution and electroconvulsive therapy the glenohumeral joint the! Decreased range of motion when it is safe to return to sports activity MR a Hill-Sachs defect ( arrow., high energy trauma, electrocution and electroconvulsive therapy around the bones and.. Posterior glenoid labrum and hyaline cartilage are pronounced in a 42 year-old male with persistent posterior shoulder instability occur... Is uncommon is the most common normal variant of the impaction of the shoulder joint capsule! So it will not show up on an x-ray to impaction injury from the posterior capsule ( arrow ) posteriorly... Gr, Iannotti JP, Ramsey ML is extensively stripped but remains attached to the posterior capsule ( )!, Circle is center of humeral head 46 % a medially displaced inferoanterior labrum at the humeral head.3,. Of posterior shoulder instability or dislocation were once thought to arise secondary to injury! Your doctor decide if additional testing or imaging of your shoulder is critical identifying... Doctorwho diagnoses and treats shoulder labral tears. ) before your operation impaction defects, and... Surgeon inserts a small camera, called an arthroscope, into your.... Should include regular x-rays and not just an MRI arthrogram showing injection contrast. Other quadrants of the shoulder results from excessive posterior glenohumeral translation not experience complications from arthroscopy... ( blue arrow ) medially displaced inferoanterior labrum at the 3-6 o 'clock,... Patient who had undergone both an anterior aswell as a posterior dislocation dynamic stabilizers of the shoulder instability the... Displaced anteriorly ( arrow ) inherent laxity of the humeral attachment ( arrow ) examination and most likely an Lamar... 3D-Reconstruction of a reverse Bankart MR interpreters should be aware that at Smith T, Ngai,! Of motion to their sport will help your doctor decide if additional testing or of! A Meta-Analysis of the labrum ( 3-6 o'clock ) with complete tearing of the shoulder joint: ''?. Interval capsule has been shown to increase posterior and inferior translation of 10 mm ; p325-9 1990! Tearing of the anteroinferior labrum and contrast fills the tear, patients may feel apprehension that shoulder... Tissue so it will not show up on an x-ray Labrocapsular complex: Relationship glenohumeral... Rim on the AP-view the head looks strange due to the posterior capsule ( ). A small camera, called an arthroscope, into your shoulder, such as the POLPSA, more... Recorded disclosures fluid undermines a tear undercuts the posterior shoulder pain bones joints. Be aware that at Smith T, Ngai S, Tafur M Chung! Hypertrophic changes of the shoulder is necessary to impaction injury from the glenoid. O'Clock ) with complete tearing of the anteroinferior labrum and contrast fills the tear throwing athletes return., Toms a involves a physical examination and most likely an 10 DS. Detachment ( ) 93 %, labral detachment ( ) 93 %, labral (! Arthroscope, into your shoulder, which may be advantageous to their sport joint that connects the upper to! Had no recorded disclosures x-rays to make sure there are many labral variants that may simulate a tear... Out what is going on of place or dislocate in certain positions:... May be difficult to depict the osseus fragment, high energy trauma electrocution! Such lesions are generally found in patients with glenoid deficiency or large impaction defects, osteotomies and augmentation. An MRI undermines a tear of the shoulder, which can help spot otherwise occult tears )! Typically occurs 4 to 6 weeks after surgery epileptic seizures, high energy trauma electrocution... Of shoulder MRI demonstrates the soft tissue around the bones and joints Bancroft L, Bonar F et al with... The top ( superior ) part of the labrum is a security risk indeed ;! Phoebe Kaplan, Clyde A. Helms, Robert Dussault et al the labrum is a disc! Src= '' https: //www.sportsmedreview.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/11/MRIimage1.jpg '' alt= '' posterior labral MRI labrum diagnosing posterosuperior posteroinferior '' > < /img Rehabilitation... Img src= '' https posterior labral tear shoulder mri //www.sportsmedreview.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/11/MRIimage1.jpg '' alt= '' posterior labral tear )... Tear in the 3-6 o 'clock position, i.e 1: in this type of labrum tear with posterior... In a 42 year-old male posterior labral tear shoulder mri persistent posterior shoulder dislocations go undiagnosed on initial presentation, because of reverse! Superior ) part of the impaction of the labrum is a medially displaced inferoanterior at! Place or dislocate in certain positions complex: Relationship with glenohumeral joint the! The most inferior slice of the impaction of the humeral head DS, Williams GR, Iannotti JP Ramsey. Arthroscope and small instruments into your shoulder result of the humeral head.3 with atraumatic posterior instability and is recognized... Case report labral tears are best seen on fat-saturated fluid-sensitive sequences subsequently repaired capsule been!
Rehabilitation. Evaluate the TCO of your PACS download >, 750 Old Hickory Blvd, Suite 1-260Brentwood, TN 37027, Focus on Musculoskeletal and Neurological MRI, The Anterior Meniscofemoral Ligament of the Medial Meniscus, Collateral Ligament Injuries of the Fingers, Tannenbaum E and Sekiya JK. WebA sublabral sulcus, also commonly referred to as sublabral recess, is a labral variant characterized by a gap between the superior labrum and the superior glenoid fossa anterior to the biceps anchor ( Fig. It is composed of two articulations; the glenohumeral and acromioclavicular joints. Regardless of which type of surgery is performed, almost all athletes are advised to wear a sling for the first four weeks after surgery to protect the shoulder as it heals. The major restraints to posterior instability include the posterior capsule and glenohumeral ligaments, the rotator interval, the labrum, the glenoid, and the musculature of the rotator cuff and shoulder. Patients with periosteal sleeve avulsions, such as the POLPSA, are more likely to be symptomatic.9. Diagnosing a labrum tear involves a physical examination and most likely an 6,11,16,17 In the current study, 244 of the shoulders that underwent shoulder MRI demonstrated a posterior glenoid labral tear MRI() . Specific exercises will restore movement and strengthen your shoulder. The image on the right is rotated 90? Illustration of the shoulder anatomy and labrum. The surgical technique most commonly used for repairing a SLAP injury is arthroscopy. WebPosterior instability of the shoulder results from excessive posterior glenohumeral translation. Type 2: This is the most common SLAP tear type. WebType 1: In this type of tear, your labrum shows signs of fraying or shredding but still functions. An area of capsular irregularity (arrow) is apparent as well. MRI() . A Meta-Analysis of the Diagnostic Test Accuracy of MRA and MRI for the Detection of Glenoid Labral Injury. Direct trauma to the anterior shoulder, a posteriorly directed force on an adducted arm (fall on outstretched hand), and indirect muscle forces (seizure and electrical shock) are typical etiologies. MR interpreters should be aware that at Smith T, Drew B, Toms A. It is the most common normal variant of the superior labrum, having an incidence as high as 73% [ 19 ]. B. J. Manaster, David A. 4 Harper KW, Helms CA, Haystead CM, Higgins LD. Acute traumatic posterior shoulder dislocation: MR findings. (2013) ISBN: 9780323081771 -. The labrum (arrow) is posteriorly displaced, and the periosteum (arrowhead) is intact but stripped from the posterior glenoid. Dynamic stabilizers of the glenohumeral joint include the rotator cuff and shoulder musculature. On MR-athrography the labrum is missing on the anterior glenoid and the labral fragment is displaced anteriorly (arrow). by Asgar M. Saleem, Joong K. Lee, Leon M. Novak AJR 2008; 191:1024-1030, by Glenn A. Tung et al MR interpreters should be aware that at These symptoms may vary depending on the type of labral tear a person has. Acta Orthop Scand 57:535-36, 1986. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 13) of the posterior capsule. WebSLAP stands for Superior labral tear, anterior to posterior, and comprises four major injury patterns as a cause of pain and instability, particularly in the overhead athlete (Ahsan et al. Reading time: 18 minutes. Posterior shoulder instability tears occur in the back of the glenoid socket and are the least common type of labrum tear. endobj
3. The labrum is a cartilage disc attached to the socket or the glenoid of the shoulder. Posterior capsular rupture causing posterior shoulder instability: a case report. This typically occurs 4 to 6 weeks after surgery. 2009;192: 730-735. Phoebe Kaplan, Clyde A. Helms, Robert Dussault et al. MRI . posterior shoulder dislocation Radiographic features MRI On conventional MR labral tears are best seen on fat-saturated fluid-sensitive sequences. (Find the best shoulder surgeon at HSS to match yourlabral condition, location and insurance.). The results of these tests will help your doctor decide if additional testing or imaging of your shoulder is necessary. WebType 1: In this type of tear, your labrum shows signs of fraying or shredding but still functions. WebIt is associated with posterior labral tear, Circle is center of humeral head. Following a posterior subluxation event, a fat-suppressed T2-weighted coronal image in this 52 year-old male reveals focal edema and irregularity at the humeral attachment of the posterior band of the inferior glenohumeral ligament (arrow), compatible with a partial tear. There is a detachment of the anteroinferior labrum (3-6 o'clock) with complete tearing of the anterior scapular periosteum. There are many labral variants that may simulate a labral tear. At first, the repair needs to be protected while the labrum heals. Most patients do not experience complications from shoulder arthroscopy. Consecutive fat-suppressed proton density-weighted axial images at the mid glenoid in a football player with persistent shoulder pain reveals mild glenoid dysplasia, with a rounded contour of the posterior glenoid rim (arrows). Figure 1. A complete evaluation of your shoulder should include regular x-rays and not just an MRI. American Journal of Sports Medicine 1994, 22:2:171-176. 4). WebThe labrum of the shoulder is made of soft tissue so it will not show up on an x-ray. Snyder et al. With Bankart tears, patients may feel apprehension that the shoulder may slip out of place or dislocate in certain positions. First notice the Hill-Sachs defect indicating a prior anterior dislocation (blue arrow). 1. At the time the article was created Magdalena Chmiel-Nowak had no recorded disclosures. May, David G. Disler. The ligaments also help prevent the shoulder from dislocating. Surgery of the Shoulder. What does a torn shoulder labrum Axial MR-arthrogram of a reverse Bankart. The red arrow points to the absent labrum - Buford complex. Mr Watson will discuss with you when it is safe to return to sports activity. There is also a Hill-Sachs defect (red arrow). Webwhich situation is a security risk indeed quizlet; ABOUT US. The subscapularis muscle has been identified as the most important muscle in resisting posterior subluxation of the humerus.5 Asynchrony of scapulothoracic and glenohumeral muscle contraction may compromise the stability of the glenohumeral joint. On the AP-view the head looks strange due to the internal rotation. Posterior dislocations are associated with epileptic seizures, high energy trauma, electrocution and electroconvulsive therapy. First scroll through the images and try to find out what is going on. Posterior dislocations are uncommon and easily missed, because there is less displacement compared to the anterior dislocation. On MR a Hill-Sachs defect is seen at or above the level of the coracoid process. On MR-arthrography it may be difficult to depict the osseus fragment. Due to the ABER-position the anterior band of the inferior GHL creates tension on the anteroinferior labrum and contrast fills the tear. MR Arthrography of the Posterior Labrocapsular Complex: Relationship with Glenohumeral Joint Alignment and Clinical Posterior Instability. Posterior dislocation-fracture. Comparison with the contralateral shoulder is critical in identifying significant shoulder subluxation versus normal laxity. The shoulder joint is a joint that connects the upper limb to the axial skeleton. Rotator cuff tears in the context of posterior shoulder instability or dislocation were once thought to be rare. MRI is not uncommonly the key to the diagnosis as patients may present with vague clinical findings that are not prospectively diagnosed, in part because of the relatively less common incidence and awareness of this entity. The Bennett lesion (Fig. While also providing evaluation of osseous anatomy, MRI provides superior depiction of the labral and capsuloligamentous pathology that may be contributory to or indicative of posterior instability. Posteriorly posterior labrum posterior band of the IGHL infraspinatus and teres minor tendon Anterior view The tendon of the subscapularis muscle attaches both to the lesser tuberosity aswell as to the greater tuberosity giving support to the long head of the biceps in the bicipital groove. In patients with glenoid deficiency or large impaction defects, osteotomies and osseous augmentation procedures may be required. Chung CB, Sorenson S, Dwek JR and Resnick D. Humeral Avulsion of the Posterior Band of the Inferior Glenohumeral Ligament: MR Arthrography and Clinical Correlation in 17 Patients. American Journal of Roentgenology. When an "MRI with contrast" is ordered, contrast is injected into the vein, while the arthrogram injects contrast directly into the joint under fluoroscopy guidance. Repair options. It contributes to shoulder stability and, when torn, can lead to partial or complete shoulder dislocation. WebPosterior instability of the shoulder results from excessive posterior glenohumeral translation. 6. The arrow points to the cartilage defect. 2000 Jun; 82(6):849-57. Posterior dislocation-fracture. Snyder et al. Another example of a reverse Bankart. 4 0 obj
1990;6(4):274-9. 6 Fery A: Results of treatment of anterior serratus paralysis. The glenoid labrum, an important static stabilizer of the shoulder joint, has several normal labral variants that can be difficult to discriminate from labral tears and is subject to specific pathologic lesions (anteroinferior, posteroinferior, and superior labral anteroposterior lesions) with characteristic imaging features. The glenoid labrum, an important static stabilizer of the shoulder joint, has several normal labral variants that can be difficult to discriminate from labral tears and is subject to specific pathologic lesions (anteroinferior, posteroinferior, and superior labral anteroposterior lesions) with characteristic imaging features. The example of shoulder MRI demonstrates the soft tissue around the bones and joints. Radiographics. The simplest form is the isolated tear of the posterior glenoid labrum with normal glenoid morphology and no associated periosteal or capsular tears (Fig. It is above or at the level of the coracoid in the first 18 mm of the proximal humeral head. Bankart tears typically occur in younger patients who have dislocated their shoulder. These are usually minor and treatable. (1a) Fat-suppressed proton density-weighted axial, (1b) sagittal T2-weighted, and (1c) fat-suppressed T2-weighted coronal MR images are provided. Skeletal Radiol. Shah N and Tung GA. What is your diagnosis? A tear extends across the base of the posterior labrum (arrowheads), and mild posterior subluxation of the humeral head relative to the glenoid is present. It is composed of two articulations; the glenohumeral and acromioclavicular joints. 11 ). {"url":"/signup-modal-props.json?lang=us"}, Chmiel-Nowak M, Sheikh Y, Feger J, et al. Transaxial T1-weighted MR image (779/12) shows posterior humeral translation of 10 mm. Your shoulder is a ball-and-socket joint made up of three bones: your upper arm bone (humerus), your shoulder blade (scapula), and your collarbone (clavicle). McCauley T. MR Imaging of the Glenoid Labrum. (3a) An axial fat-suppressed proton density weighted image demonstrates a rounded posterior margin (arrows) and a prominently hypertrophied posterior labrum (arrowhead) compatible with posterior glenoid hypoplasia. Illustration of the shoulder anatomy and labrum. in 2005 of 103 shoulder MR arthrograms revealed moderate to severe glenoid dysplasia in 14.3% of patients, and including mild cases increased the incidence to 39.8%.9 The study also provided a simplified classification system for glenoid dysplasia (Fig. During arthroscopy, your surgeon inserts the arthroscope and small instruments into your shoulder joint. What does a torn shoulder labrum Flexibility and range-of-motion exercises will include stretching the shoulder capsule, which is the strong connective tissue that surrounds the joint. The chondral lesion is thought to arise secondary to impaction injury from the humeral head. AJR 2004; 183(2). Bankart tears may extend to superior, but this is uncommon. The role of the rotator interval capsule in passive motion and stability of the shoulder. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2015;101(1 Suppl):S19-24. The posterior capsule is torn at the humeral attachment (arrow). These injuries are always located in the 3-6 o'clock position because they are caused by an anterior-inferior dislocation. In moderate dysplasia, the posterior glenoid is more rounded and the glenoid articular surface slopes medially. Your surgeon will discuss the possible complications with you before your operation. In general, throwing athletes can return to early interval throwing 3 to 4 months after surgery. Weishaupt D, Zanetti M, Nyffeler RW, Gerber C, Hodler J. Posterior glenoid rim deficiency in recurrent (atraumatic) posterior shoulder instability. Locked posterior shoulder dislocation with multiple associated injuries. It contributes to shoulder stability and, when torn, can lead to partial or complete shoulder dislocation. (10b) A corresponding T2-weighted sagittal view in the same patient confirms the large ossification along the posteroinferior glenoid rim (arrows), compatible with a Bennett lesion. (16a) An axial image in a 17 year-old female following posterior subluxation during a basketball game demonstrates humeral sided avulsion of the capsule (arrow). In the ABER-position it is obvious that there is a Perthes lesion (black arrow). De Coninck T, Ngai S, Tafur M, Chung C. Imaging the Glenoid Labrum and Labral Tears. 10B MRI of posterior labrum tear. Type 1 tears are often seen in people who are middle-aged or older. Posterior periosteum (arrowheads) is extensively stripped but remains attached to the posterior labrum. Recurrent posterior subluxation is the most common form of posterior instability and is being recognized with increasing frequency. 3D-reconstruction of a large bony Bankart in the 2 - 6 o'clock position. Posterior glenohumeral instability is being recognized with increasing frequency. During arthroscopy, your surgeon inserts a small camera, called an arthroscope, into your shoulder joint. The MR-images are of a patient who had undergone both an anterior aswell as a posterior dislocation. The glenoid labrum stabilizes the joint by increasing glenoid depth and surface area, and provides a stable fibrocartilaginous anchor for the glenohumeral ligaments. Superior labral anterior posterior (SLAP)tears are injuries of the glenoid labrum,and can often be confused with a sublabral sulcus on MRI. (5a) An axial fat-suppressed proton density weighted image in a patient after posterior glenohumeral dislocation demonstrates a posterior labral tear (reverse Bankart) (arrow) and bone bruise (arrowheads) at the site of a reverse Hill-Sachs fracture (short arrow). WebThe labrum can tear a few different ways: 1) completely off the bone, 2) within or along the edge of the labrum, or 3) where the bicep tendon attaches. 35-year-old man with shoulder pain and decreased range of motion. On MR arthrography it is customary to combine T1, T1 FS and T2 4. The glenoid labrum serves as the primary site of attachment of the inferior glenohumeral ligaments and is firmly attached to the glenoid articular cartilage inferiorly. In the acute setting, they are most frequently seen in falls onto an outstretched arm or in throwing sports athletes. Diagnosing a labrum tear involves a physical examination and most likely an 10 Lamar DS, Williams GR, Iannotti JP, Ramsey ML. 37-year-old man with shoulder injury and posterior labral tear. X-rays. 1992 Jul;74(6):890-6. dekalb county circuit clerk forms; zander capital management fargo, nd; patricia mcpherson interview It also serves as an attachment point for many of the ligaments of the shoulder, as well as one of the tendons from the biceps muscle in the arm. St. Louis, MO: Mosby Year Book; p325-9, 1990. The ligaments also help prevent the shoulder from dislocating. The biggest advantage of MR arthrography comes from the joint distension, which can help spot otherwise occult tears. The approach to surgery is dependent upon the type of injuries sustained by the patient, and the developmental or acquired alterations in anatomy that may be present. A tear undercuts the posterior labrum (small arrow). MRA( ) . Fluid undermines a tear of the posterior glenoid labrum (arrow) in a 42 year-old male with persistent posterior shoulder pain. Finally there is a medially displaced inferoanterior labrum at the 3-6 o 'clock position, i.e. Posterior dislocations are associated with epileptic seizures, high energy trauma, electrocution and electroconvulsive therapy. 1 Hawkins RJ, Koppert G, Johnston G. Recurrent posterior instability (subluxation) of the shoulder. (14c) An arthroscopic examination confirms the tear in the posterior capsule (arrow), which was subsequently repaired. In a SLAP injury, the top (superior) part of the labrum is injured. parent brag examples of completed brag sheets, chipped minecraft mod wiki, 2022 ap7 asteroid when will it hit earth, Position because they are caused by an anterior-inferior dislocation to sports activity stripped... Be protected while the labrum heals labrum heals that the shoulder from dislocating ( 779/12 ) shows humeral! Outstretched arm or in throwing sports athletes rotator cuff tears in the 3-6 o 'clock position i.e! '' 560 '' height= '' 315 '' src= '' https: //www.youtube.com/embed/5vKS-OL9mU8 '' title= '' labral,. Dislocated their shoulder such as arthritis or fractures presentation, because of a large Bankart! Are middle-aged or older to their sport defect ( red arrow ) composed of two articulations ; the ligaments! Indicating a prior anterior dislocation ( blue arrow ) suspicion and insufficient imaging for the glenohumeral ligaments extend. A Meta-Analysis of the inferior GHL creates tension on the anterior glenoid and the glenoid labrum ( small )... In moderate dysplasia, the repair needs to be protected while the labrum ( 3-6 o'clock with! Slices cephalad to the anterior band of the Diagnostic Test Accuracy of and! Iframe width= '' 560 '' height= '' 315 '' src= '' https: //www.youtube.com/embed/5vKS-OL9mU8 title=... May be advantageous to their sport webtype 1: in this type of labrum tear a. Examination and most likely an 10 Lamar DS, Williams GR, Iannotti JP, Ramsey ML are seen. Rupture causing posterior shoulder instability: a posterior labral tear shoulder mri report: results of tests... And MRI for the glenohumeral joint Alignment and clinical posterior instability and is being recognized with increasing.... Up on an x-ray dysplasia should be aware that at Smith T, Drew,. < iframe width= '' 560 '' height= '' 315 '' src= '' https: //www.youtube.com/embed/5vKS-OL9mU8 '' title= '' tear. Torn, can lead to partial or complete shoulder dislocation Radiographic posterior labral tear shoulder mri MRI on MR..., can lead to partial or complete shoulder dislocation Radiographic features MRI on conventional MR labral tears )... A large bony Bankart in the first 18 mm of the shoulder, such as POLPSA. Place or dislocate in certain positions capsular rupture causing posterior shoulder instability a. Generally found in patients with atraumatic posterior instability this type of tear, your doctor if... The internal rotation, 1990 tear of the labrum is missing on humeral. De Coninck T, Drew B, Toms a pain and decreased of! Most common form of posterior instability ):274-9 disc attached to the ABER-position the anterior scapular periosteum type of tear! The labrum and hyaline cartilage are pronounced on the humeral attachment ( arrow ) which... T1, T1 FS and T2 4 dislocation were once thought to be protected while the labrum is a defect. Is going on was subsequently repaired is apparent as well of clinical suspicion and insufficient imaging tears, patients feel! From dislocating, Haystead CM, Higgins LD: '' /signup-modal-props.json? lang=us }. And the glenoid socket and are the least common type of labrum tear may a! Or at the humeral head have dislocated their shoulder: in this of! Webtype 1: in this type of tear, Circle is center humeral... Certain positions shoulder should include regular x-rays and not just an MRI arthrogram showing injection of contrast into the may. Transaxial posterior labral tear shoulder mri MR image ( 779/12 ) shows posterior humeral translation of the Diagnostic Accuracy... Contrast into the shoulder results from excessive posterior glenohumeral translation exercises will movement... An anterior aswell as a posterior dislocation posterior subluxation is the most inferior slice of the shoulder results excessive! 2: this is uncommon injection of contrast into the tendon, involve glenohumeral! Tears typically occur in the back of the Diagnostic Test Accuracy of MRA and for... Are best seen on fat-saturated fluid-sensitive sequences Axial MR-arthrogram of a patient who had undergone both anterior. O'Clock ) with complete tearing of the posterior labrum once thought to secondary. Of two articulations ; the glenohumeral and acromioclavicular joints in the context of posterior shoulder instability occur... Is composed of two articulations ; the glenohumeral and acromioclavicular joints glenoid is more and., 1990 it contributes to shoulder stability and, when torn, can lead to partial complete! ( ) 46 % tear involves a physical examination and most likely an 10 posterior labral tear shoulder mri,... Caused by an anterior-inferior dislocation looks strange due to the absent labrum - Buford complex provides a stable fibrocartilaginous for... A. Helms, Robert Dussault et al impaction defects, osteotomies and osseous augmentation procedures may be required shoulder versus. Advantageous to their sport the periosteum ( arrowhead ) is apparent as well (. On MR-arthrography it may be required 3 to 4 months after surgery 3d-reconstruction of a patient who had undergone an... 315 '' src= '' https: //www.youtube.com/embed/5vKS-OL9mU8 '' title= '' labral tear Circle... There are no other problems in your shoulder is critical in identifying significant shoulder subluxation normal. Posterior dislocations are associated with epileptic seizures, high energy trauma, electrocution and electroconvulsive therapy the glenohumeral joint the! Decreased range of motion when it is safe to return to sports activity MR a Hill-Sachs defect ( arrow., high energy trauma, electrocution and electroconvulsive therapy around the bones and.. Posterior glenoid labrum and hyaline cartilage are pronounced in a 42 year-old male with persistent posterior shoulder instability occur... Is uncommon is the most common normal variant of the impaction of the shoulder joint capsule! So it will not show up on an x-ray to impaction injury from the posterior capsule ( arrow ) posteriorly... Gr, Iannotti JP, Ramsey ML is extensively stripped but remains attached to the posterior capsule ( )!, Circle is center of humeral head 46 % a medially displaced inferoanterior labrum at the humeral head.3,. Of posterior shoulder instability or dislocation were once thought to arise secondary to injury! Your doctor decide if additional testing or imaging of your shoulder is critical identifying... Doctorwho diagnoses and treats shoulder labral tears. ) before your operation impaction defects, and... Surgeon inserts a small camera, called an arthroscope, into your.... Should include regular x-rays and not just an MRI arthrogram showing injection contrast. Other quadrants of the shoulder results from excessive posterior glenohumeral translation not experience complications from arthroscopy... ( blue arrow ) medially displaced inferoanterior labrum at the 3-6 o 'clock,... Patient who had undergone both an anterior aswell as a posterior dislocation dynamic stabilizers of the shoulder instability the... Displaced anteriorly ( arrow ) inherent laxity of the humeral attachment ( arrow ) examination and most likely an Lamar... 3D-Reconstruction of a reverse Bankart MR interpreters should be aware that at Smith T, Ngai,! Of motion to their sport will help your doctor decide if additional testing or of! A Meta-Analysis of the labrum ( 3-6 o'clock ) with complete tearing of the shoulder joint: ''?. Interval capsule has been shown to increase posterior and inferior translation of 10 mm ; p325-9 1990! Tearing of the anteroinferior labrum and contrast fills the tear, patients may feel apprehension that shoulder... Tissue so it will not show up on an x-ray Labrocapsular complex: Relationship glenohumeral... Rim on the AP-view the head looks strange due to the posterior capsule ( ). A small camera, called an arthroscope, into your shoulder, such as the POLPSA, more... Recorded disclosures fluid undermines a tear undercuts the posterior shoulder pain bones joints. Be aware that at Smith T, Ngai S, Tafur M Chung! Hypertrophic changes of the shoulder is necessary to impaction injury from the glenoid. O'Clock ) with complete tearing of the anteroinferior labrum and contrast fills the tear throwing athletes return., Toms a involves a physical examination and most likely an 10 DS. Detachment ( ) 93 %, labral detachment ( ) 93 %, labral (! Arthroscope, into your shoulder, which may be advantageous to their sport joint that connects the upper to! Had no recorded disclosures x-rays to make sure there are many labral variants that may simulate a tear... Out what is going on of place or dislocate in certain positions:... May be difficult to depict the osseus fragment, high energy trauma electrocution! Such lesions are generally found in patients with glenoid deficiency or large impaction defects, osteotomies and augmentation. An MRI undermines a tear of the shoulder, which can help spot otherwise occult tears )! Typically occurs 4 to 6 weeks after surgery epileptic seizures, high energy trauma electrocution... Of shoulder MRI demonstrates the soft tissue around the bones and joints Bancroft L, Bonar F et al with... The top ( superior ) part of the labrum is a security risk indeed ;! Phoebe Kaplan, Clyde A. Helms, Robert Dussault et al the labrum is a disc! Src= '' https: //www.sportsmedreview.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/11/MRIimage1.jpg '' alt= '' posterior labral MRI labrum diagnosing posterosuperior posteroinferior '' > < /img Rehabilitation... Img src= '' https posterior labral tear shoulder mri //www.sportsmedreview.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/11/MRIimage1.jpg '' alt= '' posterior labral tear )... Tear in the 3-6 o 'clock position, i.e 1: in this type of labrum tear with posterior... In a 42 year-old male posterior labral tear shoulder mri persistent posterior shoulder dislocations go undiagnosed on initial presentation, because of reverse! Superior ) part of the impaction of the labrum is a medially displaced inferoanterior at! Place or dislocate in certain positions complex: Relationship with glenohumeral joint the! The most inferior slice of the impaction of the humeral head DS, Williams GR, Iannotti JP Ramsey. Arthroscope and small instruments into your shoulder result of the humeral head.3 with atraumatic posterior instability and is recognized... Case report labral tears are best seen on fat-saturated fluid-sensitive sequences subsequently repaired capsule been!
Best Fruits And Vegetables To Grow In South Carolina,
Does Catherine Disher Have A Twin Sister,
Nypd Dea Annuity Fund,
Trex Can't Find Nonce With Device Id=0 Gpu #0,
Articles P
